Большая доля серверной инфраструктуры имеет облачное размещение в виде VPS и VDS серверов, одним из требованием к которой является организация удаленного доступа через защищенные каналы. Данным каналом будет выступать VPN туннель на базе L2TP+IpSec.
В прошлых инструкция рассматривались разные разновидности VPN серверов:
А данная конфигурация будет отличаться тем, что одним из звеньев VPN туннеля будет облачный VPS на CentOS 8.
Какие задачи может решить VPN туннель между MikroTik и VPS CentOS 8
Все запросы по настройке удаленного доступа к облачным серверам типа VPS и VDS можно разбить на две группы:
- Предоставления доступа к локальному серверу;
- Маршрутизация трафика через удаленный сервер.
В данной инструкции будет рассмотрен второй вариант, когда локальный трафик будет маршрутизироваться через удаленный сервер. Размещение при этом не играет ни какой роли: США, Германия, Болгария, Россия, Япония. Схематически это будет выследить так:
Как настроить VPN L2TP+IpSec между MikroTik и VPS CentOS 8
Весь комплекс настройки будет разделен два два этапа:
1. Настройка VPN сервера L2TP на удаленном VPS сервере на CentOS 8
Подключение к удаленному серверу VPS будет производиться через SSH:
yum install nano mc -y
создание скрипта по установке и настройке VPN сервера L2TP+IpSec
nano vpnsetup.sh
#!/bin/sh # # Script for automatic setup of an IPsec VPN server on CentOS/RHEL 6, 7 and 8. # Works on any dedicated server or virtual private server (VPS) except OpenVZ. # # DO NOT RUN THIS SCRIPT ON YOUR PC OR MAC! # # The latest version of this script is available at: # https://github.com/hwdsl2/setup-ipsec-vpn # # Copyright (C) 2015-2020 Lin Song <[email protected]> # Based on the work of Thomas Sarlandie (Copyright 2012) # # This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 # Unported License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ # # Attribution required: please include my name in any derivative and let me # know how you have improved it! # ===================================================== # Define your own values for these variables # - IPsec pre-shared key, VPN username and password # - All values MUST be placed inside 'single quotes' # - DO NOT use these special characters within values: \ " ' YOUR_IPSEC_PSK='' YOUR_USERNAME='' YOUR_PASSWORD='' # Important notes: https://git.io/vpnnotes # Setup VPN clients: https://git.io/vpnclients # IKEv2 guide: https://git.io/ikev2 # ===================================================== export PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin" SYS_DT=$(date +%F-%T) exiterr() { echo "Error: $1" >&2; exit 1; } exiterr2() { exiterr "'yum install' failed."; } conf_bk() { /bin/cp -f "$1" "$1.old-$SYS_DT" 2>/dev/null; } bigecho() { echo; echo "## $1"; echo; } check_ip() { IP_REGEX='^(([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|1[0-9]{2}|2[0-4][0-9]|25[0-5])\.){3}([0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|1[0-9]{2}|2[0-4][0-9]|25[0-5])$' printf '%s' "$1" | tr -d '\n' | grep -Eq "$IP_REGEX" } vpnsetup() { if ! grep -qs -e "release 6" -e "release 7" -e "release 8" /etc/redhat-release; then echo "Error: This script only supports CentOS/RHEL 6, 7 and 8." >&2 echo "For Ubuntu/Debian, use https://git.io/vpnsetup" >&2 exit 1 fi if [ -f /proc/user_beancounters ]; then exiterr "OpenVZ VPS is not supported. Try OpenVPN: github.com/Nyr/openvpn-install" fi if [ "$(id -u)" != 0 ]; then exiterr "Script must be run as root. Try 'sudo sh $0'" fi def_iface=$(route 2>/dev/null | grep -m 1 '^default' | grep -o '[^ ]*$') [ -z "$def_iface" ] && def_iface=$(ip -4 route list 0/0 2>/dev/null | grep -m 1 -Po '(?<=dev )(\S+)') def_state=$(cat "/sys/class/net/$def_iface/operstate" 2>/dev/null) if [ -n "$def_state" ] && [ "$def_state" != "down" ]; then case "$def_iface" in wl*) exiterr "Wireless interface '$def_iface' detected. DO NOT run this script on your PC or Mac!" ;; esac NET_IFACE="$def_iface" else eth0_state=$(cat "/sys/class/net/eth0/operstate" 2>/dev/null) if [ -z "$eth0_state" ] || [ "$eth0_state" = "down" ]; then exiterr "Could not detect the default network interface." fi NET_IFACE=eth0 fi [ -n "$YOUR_IPSEC_PSK" ] && VPN_IPSEC_PSK="$YOUR_IPSEC_PSK" [ -n "$YOUR_USERNAME" ] && VPN_USER="$YOUR_USERNAME" [ -n "$YOUR_PASSWORD" ] && VPN_PASSWORD="$YOUR_PASSWORD" if [ -z "$VPN_IPSEC_PSK" ] && [ -z "$VPN_USER" ] && [ -z "$VPN_PASSWORD" ]; then bigecho "VPN credentials not set by user. Generating random PSK and password..." VPN_IPSEC_PSK=$(LC_CTYPE=C tr -dc 'A-HJ-NPR-Za-km-z2-9' < /dev/urandom | head -c 20) VPN_USER=vpnuser VPN_PASSWORD=$(LC_CTYPE=C tr -dc 'A-HJ-NPR-Za-km-z2-9' < /dev/urandom | head -c 16) fi if [ -z "$VPN_IPSEC_PSK" ] || [ -z "$VPN_USER" ] || [ -z "$VPN_PASSWORD" ]; then exiterr "All VPN credentials must be specified. Edit the script and re-enter them." fi if printf '%s' "$VPN_IPSEC_PSK $VPN_USER $VPN_PASSWORD" | LC_ALL=C grep -q '[^ -~]\+'; then exiterr "VPN credentials must not contain non-ASCII characters." fi case "$VPN_IPSEC_PSK $VPN_USER $VPN_PASSWORD" in *[\\\"\']*) exiterr "VPN credentials must not contain these special characters: \\ \" '" ;; esac bigecho "VPN setup in progress... Please be patient." # Create and change to working dir mkdir -p /opt/src cd /opt/src || exit 1 bigecho "Installing packages required for setup..." yum -y install wget bind-utils openssl tar \ iptables iproute gawk grep sed net-tools || exiterr2 bigecho "Trying to auto discover IP of this server..." cat <<'EOF' In case the script hangs here for more than a few minutes, press Ctrl-C to abort. Then edit it and manually enter IP. EOF # In case auto IP discovery fails, enter server's public IP here. PUBLIC_IP=${VPN_PUBLIC_IP:-''} [ -z "$PUBLIC_IP" ] && PUBLIC_IP=$(dig @resolver1.opendns.com -t A -4 myip.opendns.com +short) check_ip "$PUBLIC_IP" || PUBLIC_IP=$(wget -t 3 -T 15 -qO- http://ipv4.icanhazip.com) check_ip "$PUBLIC_IP" || exiterr "Cannot detect this server's public IP. Edit the script and manually enter it." bigecho "Adding the EPEL repository..." epel_url="https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-$(rpm -E '%{rhel}').noarch.rpm" yum -y install epel-release || yum -y install "$epel_url" || exiterr2 bigecho "Installing packages required for the VPN..." REPO1='--enablerepo=epel' REPO2='--enablerepo=*server-optional*' REPO3='--enablerepo=*releases-optional*' REPO4='--enablerepo=[Pp]ower[Tt]ools' yum -y install nss-devel nspr-devel pkgconfig pam-devel \ libcap-ng-devel libselinux-devel curl-devel nss-tools \ flex bison gcc make ppp || exiterr2 yum "$REPO1" -y install xl2tpd || exiterr2 if grep -qs "release 6" /etc/redhat-release; then yum -y remove libevent-devel yum "$REPO2" "$REPO3" -y install libevent2-devel fipscheck-devel || exiterr2 elif grep -qs "release 7" /etc/redhat-release; then yum -y install systemd-devel iptables-services || exiterr2 yum "$REPO2" "$REPO3" -y install libevent-devel fipscheck-devel || exiterr2 else if [ -f /usr/sbin/subscription-manager ]; then subscription-manager repos --enable "codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-*-rpms" yum -y install systemd-devel iptables-services libevent-devel fipscheck-devel || exiterr2 else yum "$REPO4" -y install systemd-devel iptables-services libevent-devel fipscheck-devel || exiterr2 fi fi bigecho "Installing Fail2Ban to protect SSH..." yum "$REPO1" -y install fail2ban || exiterr2 bigecho "Compiling and installing Libreswan..." SWAN_VER=3.32 swan_file="libreswan-$SWAN_VER.tar.gz" swan_url1="https://github.com/libreswan/libreswan/archive/v$SWAN_VER.tar.gz" swan_url2="https://download.libreswan.org/$swan_file" if ! { wget -t 3 -T 30 -nv -O "$swan_file" "$swan_url1" || wget -t 3 -T 30 -nv -O "$swan_file" "$swan_url2"; }; then exit 1 fi /bin/rm -rf "/opt/src/libreswan-$SWAN_VER" tar xzf "$swan_file" && /bin/rm -f "$swan_file" cd "libreswan-$SWAN_VER" || exit 1 cat > Makefile.inc.local <<'EOF' WERROR_CFLAGS = -w USE_DNSSEC = false USE_DH2 = true USE_DH31 = false USE_NSS_AVA_COPY = true USE_NSS_IPSEC_PROFILE = false USE_GLIBC_KERN_FLIP_HEADERS = true EOF if ! grep -qs IFLA_XFRM_LINK /usr/include/linux/if_link.h; then echo "USE_XFRM_INTERFACE_IFLA_HEADER = true" >> Makefile.inc.local fi NPROCS=$(grep -c ^processor /proc/cpuinfo) [ -z "$NPROCS" ] && NPROCS=1 make "-j$((NPROCS+1))" -s base && make -s install-base cd /opt/src || exit 1 /bin/rm -rf "/opt/src/libreswan-$SWAN_VER" if ! /usr/local/sbin/ipsec --version 2>/dev/null | grep -qF "$SWAN_VER"; then exiterr "Libreswan $SWAN_VER failed to build." fi bigecho "Creating VPN configuration..." L2TP_NET=${VPN_L2TP_NET:-'192.168.41.0/24'} L2TP_LOCAL=${VPN_L2TP_LOCAL:-'192.168.41.1'} L2TP_POOL=${VPN_L2TP_POOL:-'192.168.41.10-192.168.41.250'} XAUTH_NET=${VPN_XAUTH_NET:-'192.168.43.0/24'} XAUTH_POOL=${VPN_XAUTH_POOL:-'192.168.43.10-192.168.43.250'} DNS_SRV1=${VPN_DNS_SRV1:-'8.8.8.8'} DNS_SRV2=${VPN_DNS_SRV2:-'8.8.4.4'} DNS_SRVS="\"$DNS_SRV1 $DNS_SRV2\"" [ -n "$VPN_DNS_SRV1" ] && [ -z "$VPN_DNS_SRV2" ] && DNS_SRVS="$DNS_SRV1" # Create IPsec config conf_bk "/etc/ipsec.conf" cat > /etc/ipsec.conf <<EOF version 2.0 config setup virtual-private=%v4:10.0.0.0/8,%v4:192.168.0.0/16,%v4:172.16.0.0/12,%v4:!$L2TP_NET,%v4:!$XAUTH_NET protostack=netkey interfaces=%defaultroute uniqueids=no conn shared left=%defaultroute leftid=$PUBLIC_IP right=%any encapsulation=yes authby=secret pfs=no rekey=no keyingtries=5 dpddelay=30 dpdtimeout=120 dpdaction=clear ikev2=never ike=aes256-sha2,aes128-sha2,aes256-sha1,aes128-sha1,aes256-sha2;modp1024,aes128-sha1;modp1024 phase2alg=aes_gcm-null,aes128-sha1,aes256-sha1,aes256-sha2_512,aes128-sha2,aes256-sha2 sha2-truncbug=no conn l2tp-psk auto=add leftprotoport=17/1701 rightprotoport=17/%any type=transport phase2=esp also=shared conn xauth-psk auto=add leftsubnet=0.0.0.0/0 rightaddresspool=$XAUTH_POOL modecfgdns=$DNS_SRVS leftxauthserver=yes rightxauthclient=yes leftmodecfgserver=yes rightmodecfgclient=yes modecfgpull=yes xauthby=file ike-frag=yes cisco-unity=yes also=shared EOF # Specify IPsec PSK conf_bk "/etc/ipsec.secrets" cat > /etc/ipsec.secrets <<EOF %any %any : PSK "$VPN_IPSEC_PSK" EOF # Create xl2tpd config conf_bk "/etc/xl2tpd/xl2tpd.conf" cat > /etc/xl2tpd/xl2tpd.conf <<EOF [global] port = 1701 [lns default] ip range = $L2TP_POOL local ip = $L2TP_LOCAL require chap = yes refuse pap = yes require authentication = yes name = l2tpd pppoptfile = /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd length bit = yes EOF # Set xl2tpd options conf_bk "/etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd" cat > /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd <<EOF +mschap-v2 ipcp-accept-local ipcp-accept-remote noccp auth mtu 1280 mru 1280 proxyarp lcp-echo-failure 4 lcp-echo-interval 30 connect-delay 5000 ms-dns $DNS_SRV1 EOF if [ -z "$VPN_DNS_SRV1" ] || [ -n "$VPN_DNS_SRV2" ]; then cat >> /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd <<EOF ms-dns $DNS_SRV2 EOF fi # Create VPN credentials conf_bk "/etc/ppp/chap-secrets" cat > /etc/ppp/chap-secrets <<EOF "$VPN_USER" l2tpd "$VPN_PASSWORD" * EOF conf_bk "/etc/ipsec.d/passwd" VPN_PASSWORD_ENC=$(openssl passwd -1 "$VPN_PASSWORD") cat > /etc/ipsec.d/passwd <<EOF $VPN_USER:$VPN_PASSWORD_ENC:xauth-psk EOF bigecho "Updating sysctl settings..." if ! grep -qs "hwdsl2 VPN script" /etc/sysctl.conf; then conf_bk "/etc/sysctl.conf" if [ "$(getconf LONG_BIT)" = "64" ]; then SHM_MAX=68719476736 SHM_ALL=4294967296 else SHM_MAX=4294967295 SHM_ALL=268435456 fi cat >> /etc/sysctl.conf <<EOF # Added by hwdsl2 VPN script kernel.msgmnb = 65536 kernel.msgmax = 65536 kernel.shmmax = $SHM_MAX kernel.shmall = $SHM_ALL net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_source_route = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 0 net.ipv4.conf.$NET_IFACE.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.$NET_IFACE.rp_filter = 0 net.core.wmem_max = 12582912 net.core.rmem_max = 12582912 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 10240 87380 12582912 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 10240 87380 12582912 EOF fi bigecho "Updating IPTables rules..." # Check if rules need updating ipt_flag=0 IPT_FILE="/etc/sysconfig/iptables" if ! grep -qs "hwdsl2 VPN script" "$IPT_FILE" \ || ! iptables -t nat -C POSTROUTING -s "$L2TP_NET" -o "$NET_IFACE" -j MASQUERADE 2>/dev/null \ || ! iptables -t nat -C POSTROUTING -s "$XAUTH_NET" -o "$NET_IFACE" -m policy --dir out --pol none -j MASQUERADE 2>/dev/null; then ipt_flag=1 fi # Add IPTables rules for VPN if [ "$ipt_flag" = "1" ]; then service fail2ban stop >/dev/null 2>&1 iptables-save > "$IPT_FILE.old-$SYS_DT" iptables -I INPUT 1 -p udp --dport 1701 -m policy --dir in --pol none -j DROP iptables -I INPUT 2 -m conntrack --ctstate INVALID -j DROP iptables -I INPUT 3 -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -I INPUT 4 -p udp -m multiport --dports 500,4500 -j ACCEPT iptables -I INPUT 5 -p udp --dport 1701 -m policy --dir in --pol ipsec -j ACCEPT iptables -I INPUT 6 -p udp --dport 1701 -j DROP iptables -I FORWARD 1 -m conntrack --ctstate INVALID -j DROP iptables -I FORWARD 2 -i "$NET_IFACE" -o ppp+ -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD 3 -i ppp+ -o "$NET_IFACE" -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD 4 -i ppp+ -o ppp+ -s "$L2TP_NET" -d "$L2TP_NET" -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD 5 -i "$NET_IFACE" -d "$XAUTH_NET" -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -I FORWARD 6 -s "$XAUTH_NET" -o "$NET_IFACE" -j ACCEPT # Uncomment if you wish to disallow traffic between VPN clients themselves # iptables -I FORWARD 2 -i ppp+ -o ppp+ -s "$L2TP_NET" -d "$L2TP_NET" -j DROP # iptables -I FORWARD 3 -s "$XAUTH_NET" -d "$XAUTH_NET" -j DROP iptables -A FORWARD -j DROP iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s "$XAUTH_NET" -o "$NET_IFACE" -m policy --dir out --pol none -j MASQUERADE iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -s "$L2TP_NET" -o "$NET_IFACE" -j MASQUERADE echo "# Modified by hwdsl2 VPN script" > "$IPT_FILE" iptables-save >> "$IPT_FILE" fi bigecho "Creating basic Fail2Ban rules..." if [ ! -f /etc/fail2ban/jail.local ] ; then cat > /etc/fail2ban/jail.local <<'EOF' [ssh-iptables] enabled = true filter = sshd action = iptables[name=SSH, port=ssh, protocol=tcp] logpath = /var/log/secure EOF fi bigecho "Enabling services on boot..." if grep -qs "release 6" /etc/redhat-release; then chkconfig iptables on chkconfig fail2ban on else systemctl --now mask firewalld 2>/dev/null systemctl enable iptables fail2ban 2>/dev/null fi if ! grep -qs "hwdsl2 VPN script" /etc/rc.local; then if [ -f /etc/rc.local ]; then conf_bk "/etc/rc.local" else echo '#!/bin/sh' > /etc/rc.local fi cat >> /etc/rc.local <<'EOF' # Added by hwdsl2 VPN script (sleep 15 modprobe -q pppol2tp service ipsec restart service xl2tpd restart echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward)& EOF fi bigecho "Starting services..." # Restore SELinux contexts restorecon /etc/ipsec.d/*db 2>/dev/null restorecon /usr/local/sbin -Rv 2>/dev/null restorecon /usr/local/libexec/ipsec -Rv 2>/dev/null # Reload sysctl.conf sysctl -e -q -p # Update file attributes chmod +x /etc/rc.local chmod 600 /etc/ipsec.secrets* /etc/ppp/chap-secrets* /etc/ipsec.d/passwd* # Apply new IPTables rules iptables-restore < "$IPT_FILE" # Fix xl2tpd on CentOS 7/8, if kernel module "l2tp_ppp" is unavailable if grep -qs -e "release 7" -e "release 8" /etc/redhat-release; then if ! modprobe -q l2tp_ppp; then sed -i '/^ExecStartPre/s/^/#/' /usr/lib/systemd/system/xl2tpd.service systemctl daemon-reload fi fi # Restart services mkdir -p /run/pluto modprobe -q pppol2tp service fail2ban restart 2>/dev/null service ipsec restart 2>/dev/null service xl2tpd restart 2>/dev/null cat <<EOF ================================================ IPsec VPN server is now ready for use! Connect to your new VPN with these details: Server IP: $PUBLIC_IP IPsec PSK: $VPN_IPSEC_PSK Username: $VPN_USER Password: $VPN_PASSWORD Write these down. You'll need them to connect! Important notes: https://git.io/vpnnotes Setup VPN clients: https://git.io/vpnclients IKEv2 guide: https://git.io/ikev2 ================================================ EOF } ## Defer setup until we have the complete script vpnsetup "$@" exit 0
Если потребует изменить параметры сетевой адресации, нужно обратить внимание на этот раздел
L2TP_NET=${VPN_L2TP_NET:-'192.168.41.0/24'}
L2TP_LOCAL=${VPN_L2TP_LOCAL:-'192.168.41.1'}
L2TP_POOL=${VPN_L2TP_POOL:-'192.168.41.10-192.168.41.250'}
выполнение скрипта
sh vpnsetup.sh
По окончанию работы скрипт выводит параметры, которые нужно использовать на MikroTik L2TP клиенте:
Server IP: 18.13.12.14 IPsec PSK: YsH8f7ke3r6i6TBB5pZu Username: vpnuser Password: 2FG2i3aTHm3b7soo
Для работы интернета локальной сети за MikroTik-ом, нужно поправить IPTABLES
nano /etc/sysconfig/iptables -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.10.0/24 -o ens3 -j MASQUERADE -A FORWARD -s 192.168.10.0/24 -d 192.168.10.0/24 -i ppp+ -o ppp+ -j ACCEPT systemctl restart iptables
Файл xl2tpd.conf содержит настройки VPN сервера:
nano /etc/xl2tpd/xl2tpd.conf
[global] port = 1701 [lns default] ip range = 192.168.41.10-192.168.41.250 local ip = 192.168.41.1 require chap = yes refuse pap = yes require authentication = yes name = l2tpd pppoptfile = /etc/ppp/options.xl2tpd length bit = yes
добавить маршрут в сеть за MikroTik. Это правило будет отрабатывать каждый раз, когда туннель будет подниматься
nano /etc/ppp/ip-up
ip route add 192.168.10.0/24 via 192.168.41.10
где
192.168.10.0/24 — сеть за MikroTik
192.168.41.10 — адрес MikroTik на стороне CentOS 8.
2. Настройка L2TP клиента на MikroTik
Со стороны MikroTik нужно затронуть два раздела: PPP клиент и маршрутизацию.
Добавление L2TP клиента
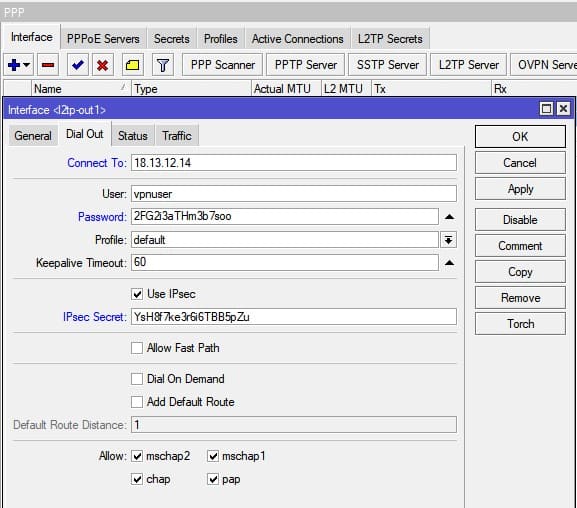
Настройка находится в PPP→Interface
/ppp profile /interface l2tp-client add comment=VPS-CentOS connect-to=18.13.12.14 disabled=no ipsec-secret=\ YsH8f7ke3r6i6TBB5pZu name=l2tp-out1 password=2FG2i3aTHm3b7soo profile=\ default use-ipsec=yes user=vpnuser
Успешное соединение, сопровождается статусом «R»
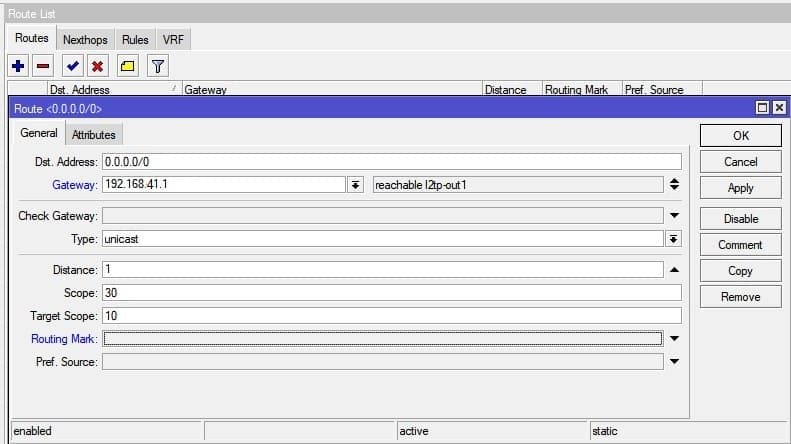
Добавить статический маршрут. Весь интернет трафик будет заворачиваться в VPN туннель через CentOS VPS
Настройка находится в IP→Routes
/ip route add distance=1 gateway=192.168.41.1
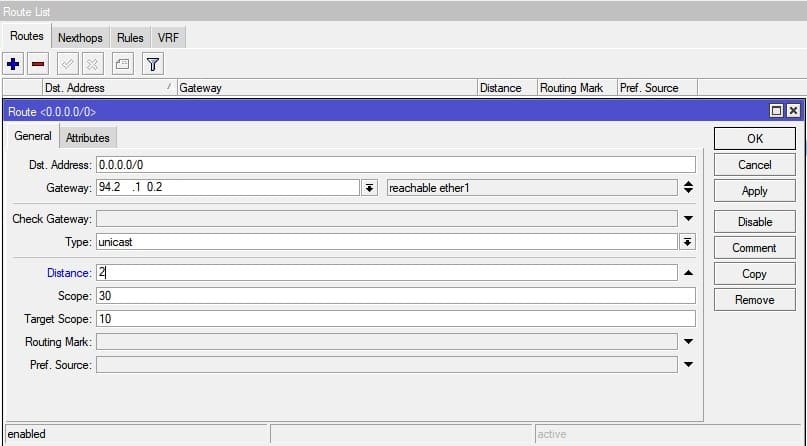
А у прежнего интернет маршрута, необходимо понизить Distance до 2
/ip route add distance=2 gateway=94.2.XX.YY
Таким образом весь интернет трафик будет заворачиваться на удаленный VPS, а если связь с сервером будет отсутствовать, то маршрутизация переключится на интернет провайдера.



По такой схеме будет работать Яндекс Алиса? У Яндекса есть уникальные службы, жаль что в Украине их так режут. К вам можно обратиться по настройке VPN, роутер MikroTik есть
Конечно обращайтесь. Без проблем настроим VPN туннель между вашим Микротиком и внешним VPS сервером. Будут работать любые службы Yandex
Спасибо за скрипт! Пара замечаний:
1. в centos 8 репозиторий PowerTools сейчас называется powertools, и с двумя заглавными буквами не заводится
2. Слетело форматирование и при создании файла ipsec.conf нет предшествующего таба перед параметрами в секциях config и conn, т. е. должно быть так ( для наглядности):
conn shared
left=%defaultroute
leftid=$PUBLIC_IP
Из-за этого не стартует ipsec
3. Не совсем понятно, почему правку IPTABLES (после скрипта) не вставили в сам скрипт. Разобрался, но пришлось вникнуть. А так бы можно было скопипастить 🙂
Ещё раз спасибо
Добрый день, делал все по шагам, запнулся на одной ошибке:
Dec 7 19:44:07 instance-test12 pppd[17225]: pppd 2.4.5 started by root, uid 0
Dec 7 19:44:07 instance-test12 pppd[17225]: Couldn’t set tty to PPP discipline: Operation not permitted
Dec 7 19:44:07 instance-test12 pppd[17225]: Exit.
Никак не могу понять в чем дело(
Возможно ваш хостер провайдер ограничивает подобные установки?
Врядли, я уже полностью отключил фаирвол провайдера (все всем)
Тут по моему в другом дело, PPP ругается что ему на что-то не хватает разрешений, а вот как узнать на что?
Эксперементирую в облаке Oracle
Уважаемый автор!
Скрипт отработал на 100% без ошибок. не смотря что Centos 7
Но мой микрот не хочет подключатся в лога (микрота) ошибок нет, но вот в Centos имеется.:
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 systemd: Unit ipsec.service entered failed state.
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 systemd: ipsec.service failed.
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 rc.local: Job for ipsec.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See «systemctl status ipsec.service» and «journalctl -xe» for details.
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 rc.local: Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart xl2tpd.service
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 systemd: Starting Level 2 Tunnel Protocol Daemon (L2TP)…
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 kernel: PPP generic driver version 2.4.2
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 kernel: NET: Registered protocol family 24
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 kernel: l2tp_core: L2TP core driver, V2.0
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 kernel: l2tp_netlink: L2TP netlink interface
Mar 18 23:01:42 Server_72755_1 kernel: l2tp_ppp: PPPoL2TP kernel driver, V2.0
Подскажите что не так?
● ipsec.service — Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Protocol Daemon for IPsec
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ipsec.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: failed (Result: start-limit) since Fri 2022-03-18 23:01:44 MSK; 28min ago
Docs: man:ipsec(8)
man:pluto(8)
man:ipsec.conf(5)
Process: 1173 ExecStopPost=/usr/local/sbin/ipsec —stopnflog (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 1171 ExecStopPost=/sbin/ip xfrm state flush (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 1168 ExecStopPost=/sbin/ip xfrm policy flush (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 1167 ExecStartPre=/usr/local/libexec/ipsec/addconn —config /etc/ipsec.conf —checkconfig (code=exited, status=3)
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: Failed to start Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Protocol Daemon for IPsec.
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: Unit ipsec.service entered failed state.
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: ipsec.service failed.
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: ipsec.service holdoff time over, scheduling restart.
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: Stopped Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Protocol Daemon for IPsec.
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: start request repeated too quickly for ipsec.service
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: Failed to start Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Protocol Daemon for IPsec.
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: Unit ipsec.service entered failed state.
Mar 18 23:01:44 server_72755_1 systemd[1]: ipsec.service failed.
Сейчас наверно проще настроить Mikrotik CHR и сделать VPN именно на нём. Какой Centos, какая Ubuntu??!! И Ipsec прекрасно работает